For Providers -- Atlas of Human Anatomy
Translated by: Ronald A. Bergman, PhD and Adel K. Afifi, MD, MS
Peer
Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed

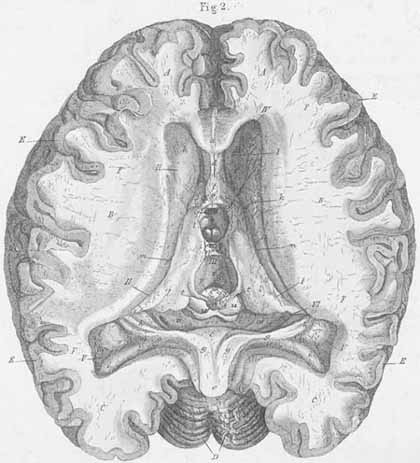
A) Frontal lobe (s. anterior cerebral lobe) [OBS].
B) Temporal lobe (s. middle cerebral lobe) [OBS].
C) Occipital lobe (s. posterior cerebral lobe) [OBS].
D) Cerebellum.
E) Cortical grey matter. Substantia corticalis (s. substantia cinereium).
F) Centrum, semiovale, white matter core, Substantia alba (s. substantia medullaris).
I. Right lateral ventricle, cella lateralis.
II. Left lateral ventricle, cella lateralis.
III. Third ventricle.
IV. Anterior horn, lateral ventricle.
V. Posterior horn, lateral horn.
VI. Inferior horn, lateral ventricle.
a) Corpus callosum (truncus with raphe).
b) Genu of corpus callosum.
c) Hippocampal commissure, forical commissure, psalterium, Commissura fornix
[on the inferior surface of the splenium of corpus callosum].
d) Septum pellucidum (with ventriculus septi pellucidum).
e) Fornix.
f) Anterior crus of the fornix.
g) Posterior crus of the fornix.
h) Pes hippocampi major (s. cornu ammonis) [with the fimbria fornix on the inner
edge].
i) Calcar avis, Pes hippocampi minor .
k) Caudate nucleus.
l) Thalamus (optic thalamus).
m) Stria terminalis (stria cornea).
n) Massa intermedia.
o) Anterior commissure.
p) Posterior commissure.
q) Infundibular recess.
r) Cerebral acqueduct, acqueduct of Sylvius (cerebral anus).
s) Pineal gland.
t) Stalk of the pineal gland.
u) Corpora quadrigemina.
v) Choroid plexus.