For Providers -- Atlas of Human Anatomy
Translated by: Ronald A. Bergman, PhD and Adel K. Afifi, MD, MS
Peer
Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed

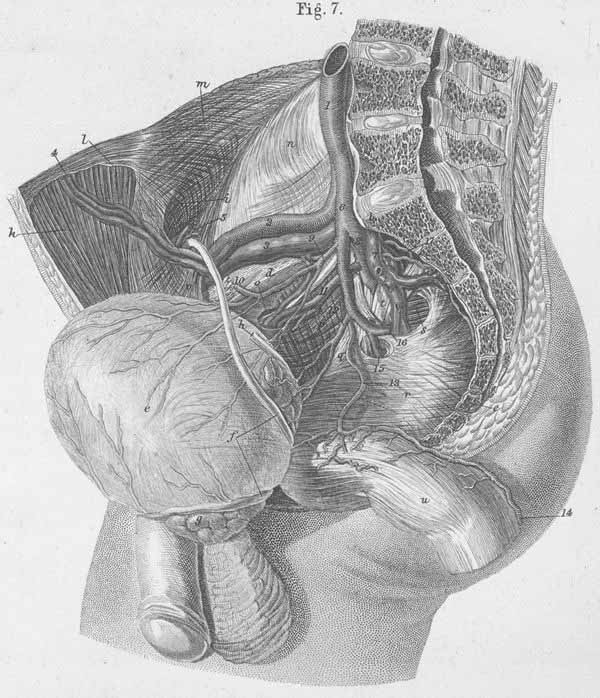
a) Four lumbar vertebrae.
b) Promontorium, pelvic.
c) Os coccyx.
d) Internal arcuate line (boundary between greater and true pelvis).
e) Urinary bladder.
f) Vas deferens.
g) Seminal vesicle.
h) Right ureter.
i) Internal inguinal anulus.
k) m. Rectus abdominis.
l) Arcuate line of the sheath of m. rectus abdominis (s. linea semicirculais
Douglasii). The lower half of m. rectus abdominis which is only covered by peritoneum.
m) Fascia transversa. The abdominal muscles are seen in overview.
n) Iliac fascia, the internal iliac and psoas major muscles are seen in overview.
o) Obturator canal, through which the obturator nerve, artery and vein pass.
p) Pelvic fascia, through which the m. obturator internus can be seen.
q) Arcus tendineus of pelvic fascia.
r) Pelvic fascia, with overview of levator ani and coccygeus muscles are seen.
s) m. piriformis.
t) Sacral plexus (s. sciatic).
u) Rectum.
v) Lacunar ligament (s. ligamentum Gimbernati).