For Providers -- Atlas of Human Anatomy
Translated by: Ronald A. Bergman, PhD and Adel K. Afifi, MD, MS
Peer
Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed

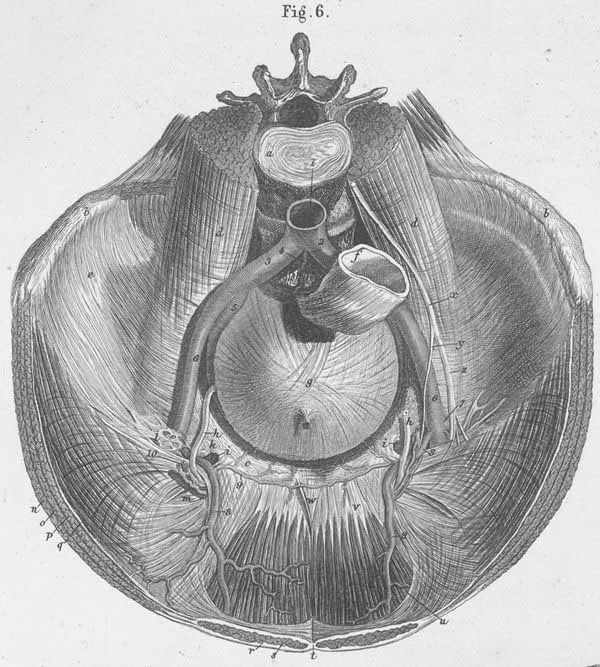
a) Vertebral disk between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae.
b) Iliac crest.
c) True pelvis, anterior rim.
d) m. Psoas (divided).
e) m. Internal iliac.
f) Rectum.
g) Urinary bladder.
h) Vas deferens.
i) Lacunar ligament (Gimbernati ligament).
k) Superior opening of femoral canal.
l) Multiple continuations of iliac fascia, which covers the blood vessels entering
the thigh.
m) Deep inguinal ring (s. internal inguinal anulus).
n) m. External abdominal oblique (cut across).
o) m. Internal abdominal oblique (cut across).
p) m. Transversus abdominis (cut across).
q) Transversalis fascia.
r) Sheath of m. Rectus abdominis.
s) m. Rectus abdominis.
t) Linea alba.
u) Arcuate line (at the end of the sheath of the rectus abdominis muscle, s.
semicircular line of Douglass).
v) m. Rectus abdominis (the part that is not covered by fascia at its distal
end).
w) Adminiaculum linea albae.
x) Genitofemoral nerve.
y) Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve.
z) Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve.