For Providers -- Atlas of Human Anatomy
Muscles of the upper and posterior abdominal and pelvic wall, the diaphragm
extending from the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity.
Translated by: Ronald A. Bergman, PhD and Adel K. Afifi, MD, MS
Peer
Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed
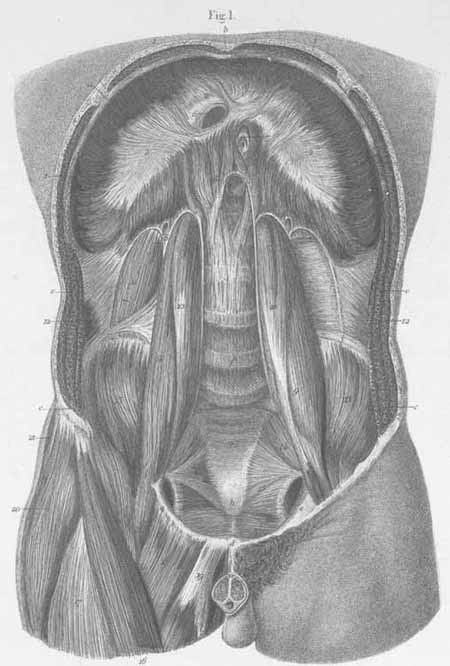
a) Inferior wall of the thorax.
b) Sternal xiphoid process.
c) Opened abdominal wall (mm. obliqui and m. transverses abdominis are seen).
d) Pubic symphysis.
e) Pubic bone, horizontal ramus.
f) Lumbar vertebra.
g) Sacral bone.
h) Coccyx.
i) Iliac crest.
- diaphragm, costal part (muscular).
- diaphragm, central tendon (s. speculum Helmontii diaphragmatis).
- diaphragm, lumbar part, medial cruz (leg).
- diaphragm, lumbar part, middle cruz
- diaphragm, lumbar part, lateral cruz (Passing between the lateral and middle
crus, sympathetic nerves, vena azygos, linkage with the vena hemiazygos; between
the medial and middle cruz, the greater splanchnic passes as well as links
of vena hemiazygos, and the lesser splanchnic nerve pierces the middle cruz).
- foramen quadratum (for the vena cava).
- foramen esophageum (for the esophagus and vagal nerves).
- Aortic hiatus (for the aorta, thoracic duct, and occasionally vena azygos
or hemiazygos.
- m. psoas major.
- m. psoas minor.
- m. quadratus lumborum.
- m. transverses abdominis (with fascia transversa).
- m. iliacus interna.
- m. pyriformis.
- m. levator ani.
- m. sartorius.
- m. rectus femoris.
- m. pectineus.
- m. adductor longus.
- m. tensor fascia lata.
- m. gluteus media.
Plate Index | Title Page

