For Providers -- Atlas of Human Anatomy
Translated by: Ronald A. Bergman, PhD and Adel K. Afifi, MD, MS
Peer
Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed

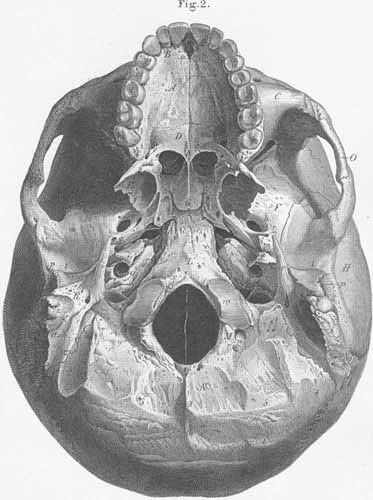
A) Palatine process of the maxilla.
B) Alveolar processes of the maxilla.
C) Maxilla bone.
D) Horizontal part of the palatine bone.
E) Pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone.
F) Greater wing of the sphenoid bone.
G) Vomer.
H) Squamous part of the temporal bone.
I) Mastoid part of the temporal bone.
K) Petrous portion of the temporal bone.
L) Basilar part of the occipital bone.
M) Condyloid part of the occipital bone.
N) Occipital part of the occipital bone.
O) Zygomatic arch.
a) Incisive foramen (incisive canal) (passage for nasopalatine artery, vein,
and nerve).
b) Posterior nasal spine (origin of the uvula).
c) Palatine foramen (passage for arteries, veins, and the palatine nerves).
d) Medial wing of the pterygoid process (pterygoid hamulus, origin of pterygopharyngeal
part of the superior pharyngeal constrictor).
e) Pterygoid fossa (origin of medial pterygoid muscle).
f) Lateral wing of the pterygoid process (origin of the m lateral pterygoid).
g) Choanae narium, posterior opening of the nose.
h) Foramen ovale (passage for the maxillary nerve).
i) Foramen spinosum (passage for middle meningeal artery and lesser superficial
petrosal nerve).
k) Inferior orbital fissure (between the greater wing of the pterygoid and maxilla;
passage of the facial ophthalmic vein, infraorbital artery, vein and nerve and
cutaneus nerve of the cheek).
l) Articular fossa (for mandibular condyle).
m) Articular tubercle.
n) Petrotympanic fissure (passage for tympanic artery, chorda tympani and m
tensor typani).
o) Eustacian tube (Auditory tube).
p) External auditory meatus.
q) Entrance to the carotid canal (passage for internal carotid artery and the
carotid nerve).
r) Styloid process (origin for mm stylohyoid, styloglossus, stylopharyngeus
and of stylohyoid ligament).
s) Stylomastoid foramen (passage for the facial nerve and for the stylomastoid
artery).
t) Cochlear aquaduct.
u) Jugular foramen (passage for internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal, vagus,
and spinal accessory nerves).
v) Petrosal fossa (for the petrosal ganglion of glossopharyngeal nerve).
w) Condyle of the occipital bone (connected to the atlas by a hinge joint).
x) Anterior condyloid foramen s. hypoglossal canal (passage for the hypoglossal
nerve).
y) Posterior condyloid foramen (passage for Santorini’s emissary vein;
often absent).
z) Mastoid process (attachment site for mm sternocleidomastoid, splenius capitis,
longissimus capitis and mm retahentes auriculae [auricularis posterior]).
a) Mastoid incisure (origin of m digastricus).
b) Mastoid foramen (passage for an emissary
vein of Santorini or posterior meningeal artery).
g) External occipital spine.
d) External occipital crest (protuberance)
(origin of ligamentun nuchae).
e) Inferior nuchal line (attachment site
for mm rectus capitis posterior major and minor, and supeior capitis oblique).
z) Superior nuchal line (attachment site
for mm trapezius, digastricus, semispinalis capitis, splenius capitis and sternocleidomastoideus).
h) Spinous process (origin of mm tensor
veli palatini and tensor tympani).