For Providers -- Atlas of Human Anatomy
Translated by: Ronald A. Bergman, PhD and Adel K. Afifi, MD, MS
Peer Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed

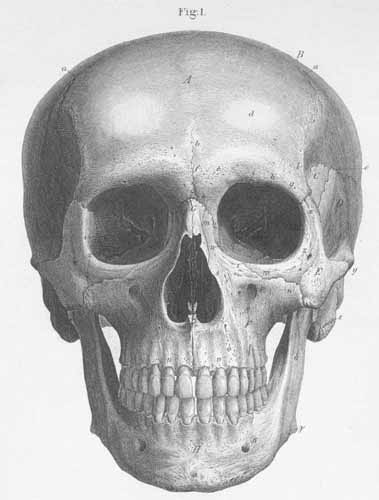
A) Frontal bone.
B) Parietal Bone.
C) Sphenoid bone, greater wing.
D) Temporal bone.
E) Zygomatic bone (origin of mm.zygomaticus major and minor).
F) Maxilla.
G) Nasal bones.
H) Mandible.
a) Coronal suture.
b) Frontal suture.
c) Squamus suture.
d) Frontal eminence.
e) Superciliary ridge (covered by m. corrugator supercilii).
f) Glabella.
g) Zygomatic process.
h) Supraorbital margin.
i) Supraorbital notch (or foramen) (for the passage of the supraorbital artery,
vein and nerve).
k) Frontal bone, nasal process.
l) Nasal Spine.
m) Nasal process of the maxilla (origin of mm frontalis, orbicularis palpebrum,
and levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, and zygomaticomaxillary suture and
medial palpebral ligament).
n) Zygomatic process of the maxilla.
o) Alveolar process of the maxilla (origin of mm. compressor, depressor nasi,
buccinator,and incisivi labii superioris and inferioris).
p) Infraorbital foramen (exit of infraorbital canal carrying the infraorbital
artery, vein, and nerve).
q) Maxillary depression (origin of m. levator anguli oris).
r) Anterior nasal spine (origin of m. orbicularis oris).
s) Nasal pyriform aperature.
t) Infraorbital margin (covered by the m. orbicularis palpebrum and origin of
m. levator labii superioris proprius).
u) Fossa of the lacrimal sac.
v) Alveolar yokes.
w) Maxillary process of the zygomatic bone (origin of m. zygomaticus minor).
x) Frontal of the zygomatic bone.
y) Temporal process of the zygomatic bone.
z) Zygomaticofacial foramen. (transmits the zygomaticofacial nerve).
a)Mentum (chin), external mental spine.
b) Mental foramen (exit for the mental
artery, vein, and nerve).
g) Mandibular angle (beginning of mm masseter
and medial pterygoid).
d) Mandibular ramus.
e) Mastoid process.
z)Optic foramen (for the optic nerve and
ophthalmic artery).
h) Superior orbital fissure. (between the
greater and lesser wings of the sphenoid bone) (passage for the ophthalmic vein,
nn. oculomotor, trochlear, ophthalmic, and abducens nerves).
q) Inferior orbital fissure (between the
greater wing of the sphenoid and maxillary bone) (passage for ophthalmic vein,
infraorbital nerve, artery, and vein, and cutaneous nerve of the cheek).
i) Zygomaticoorbital foramen (transmits
zygomaticofacial and zygomaticotemporal brs. to the temporal fossa).