ความคิดเห็นทั้งหมด : 4
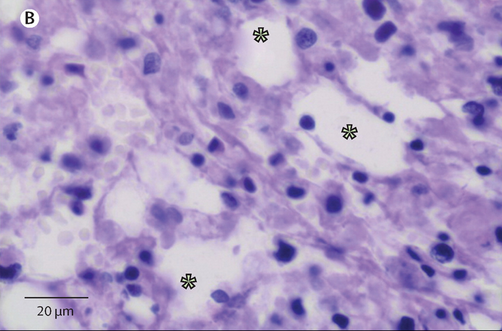
ชายอายุ 72 ปี เป็น type 2 DM ปวดท้อง และมีความผิดปกติที่กระดูก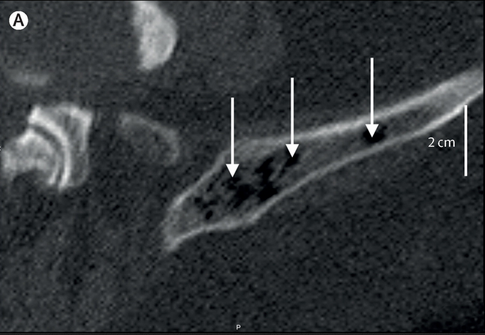 ชายอายุ 72ปีซึ่งเป็น type 2 DM มาพบแพทย์เนื่องจากมีอาการปวดท้องหลังจากหกล้มลำตัวด้านขวากระแทกพื้น. ผู้ป่วยได้รับ anticoagulants อยู่เนื่องจากมี atrial fibrillation. CT abdomen พบ hepatic haematoma. ตรวจพบ ค่า C-reactive protein และ procalcitonin concentrations สูง ซึ่งแสดงว่าน่าจะมี superinfection. ผู้ป่วยได้รับการทำ diagnostic aspiration และได้รับการรักษาด้วย IV ceftriaxone. วันรุ่งขึ้น อาการของผู้ป่วยทรุดลง แพทย์ได้เปลี่ยนยาเป็น meropenem. Follow-up CT scan พบความผิดปกติที่ pelvis และ lumbar vertebra ดังในรูป A. 1. ความผิดปกติที่กระดูกนี้คืออะไร 2. จะ manage อย่างไร Posted by : cpantip , E-mail : (chpantip@gmail.com) , Date : 2015-04-15 , Time : 16:50:50 , From IP : 172.29.3.187 |