Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) เป็น inflammatory response ที่รุนแรงมากกว่าปกติ เกิดขึ้นภายใน 3 เดือนของการเริ่มต้นรักษาด้วยยา antiretrovirus ในผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อ HIV ซึ่งสัมพันธ์กับ immune recovery โดยมีหลักฐานว่ามี sharp increase in the CD4 T-cell count ขึ้นอย่างรวดเร็วและ HIV viral load ลดลง. IRIS เกิดขึ้นในประมาณ 11% ของผู้ป่วยที่เริ่มต้นรับ effective antiretroviral therapy และพบบ่อยกว่าในผู้ป่วยที่มี initial CD4 counts น้อยกว่า 50 cells/mm3.
IRIS มักได้รับการแบ่งเป็น paradoxical และ unmasking. Paradoxical IRIS คือภาวะที่มีการเป็นรุนแรงขึ้นของ known opportunistic infection ที่ทราบอยู่แล้วทั้งที่ได้รับการรักษาอย่างเหมาะสม. Unmasking IRIS คือภาวะที่มีการแสดงใหม่ของ opportunistic infection ซึง่ถูกเปิดเผย (unmasked) หลังเริ่มการรักษาด้วยยา antiretrovirus.
จากข้อมูลของต่างประเทศ อุบัติการณ์ของ nontuberculous mycobacterial IRIS คือ ประมาณ 3.5% ในผุ้ป่วยที่เริ่มได้ antiretroviral therapy โดยที่มี CD4 counts น้อยกว่า 100 cells/mm3. ในผู้ป่วยเหล่านี้ nontuberculous M. avium-intracellulare peripheral lymphadenitis เป็น clinical presentation ที่พบบ่อยที่สุด คือพบประมาณ 1 ใน 3 ของผู้ป่วย, ประมาณ 1 ใน 3 เริ่มเป็นที่ cervical lymph nodes.
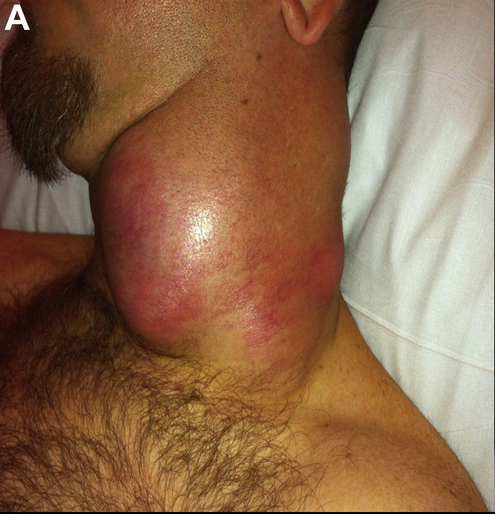
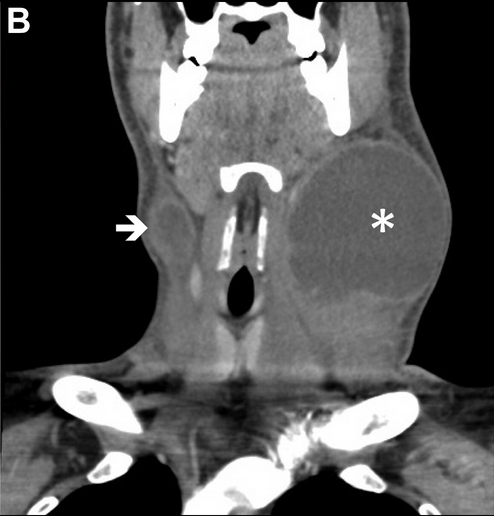
Mycobacterial cervical lymphadenitis (มีชื่อเรียกว่า scrofula) สัมพันธ์ทั้งกับ tuberculosis และ nontuberculous mycobacterial infections และแสดงออกเป็น chronic, painless neck mass ซึ่งโตขึ้นและสามารถแตกออกและระบายหนองออกได้เอง. ส่วนใหญ่ (∼90%) ของผู้ป่วย nontuberculous mycobacterial IRIS มี clinical response ต่อการให้ systemic glucocorticoid therapy ร่วมกับยารักษาการติดเชื้อนี้.
Reference: Hundemer GL, et al. Unmasking immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: nontuberculous mycobacterial scrofula.
AJM 2014;127: e5e6
Posted by : cpantip , Date : 2014-07-31 , Time : 13:09:07 , From IP : 172.29.3.148
|